Strongly Basic Anion Exchange Resins
Type I resins have trimethyl ammonium groups which impart higher basicity. In the co-current regeneration mode, the treated water will have the lowest silica leakage. Type I resins also have higher chemical stability, and can be applied at higher temparature (than Type II or acrylic based resins.)
Type II resins have dimethylethanolamine groups which impart slightly lower basicity. This provides an advantage of easier regeneration (than Type I) and slightly higher capacity.
Gel Type BS SA10 Series (Type I) and SA20 Series (Type II)
SA10A is a Type I resin with standard crosslinkage. SA12A is also a Type I resin with slightly lower crosslinkage. These resins are popularly used for water treament. SA12A is typically recommended for treatment of surface waters with troublesome organic content.
SA11A is Type I resin with low crosslinkage, and is mainly used for special applications such as sometimes used as a mixed bed or primary bed polisher anion.
SA20A is Type II resin of standard crosslinkage. It is popularly used for water treatment with its easy.
| Grade Name | SA10A | SA11A | SA12A | SA20A |
| Type | Type I | Type Ⅱ | ||
| Chemical Structure | 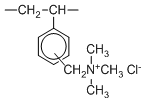 | 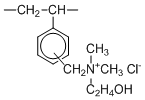 | ||
| Ionic Form As Shipped | Cl-form | |||
| Whole Bead Count | 90 min. | |||
| Shipping Density (g/L: approx.) | 670 | 685 | 670 | 715 |
| Salt Spliting Capacity (meq/mL-R) | 1.3 min | 0.85 min | 1.3 min | 1.3 min |
| Water Content (%) | 43 - 47 | 55 - 65 | 48 - 55 | 45 - 52 |
| Particle Size Distribution on 1180 μm (%) through 300 μm (%) | 5 max. 1 max. | |||
| Effective Size (mm) | 0.40 min. | |||
| Uniformity Coefficient | 1.6 max. | |||
| Operating Temperature (℃) | 60 (OH-form) max. 80 (Cl-form) max. | 40 (OH-form) max. 60 (Cl-form) max. | ||
Porous-Type BA PA300 Series (Type I)
Porous-type ion exchange resins of porous polymer matrix have good resistance against swelling and shrinking, though their exchange capacity is lower than gel-type ion exchange resins of the same degree of crosslinkage.
These are effective when highly purified effluents are needed, e.g. removal of silica to very low concentration.
They are suitable for treatments of waste waters with organic compounds. PA312 and PA316 are generally used in waste water treatments, and PA308 is used for demineralization and decolorization of sugar liquors.
Highly Porous-Type BS HPA25L (Type I)
Highly porous type resin, HPA25L, has higher crosslinkage and higher porous properties than standard PA grade resins. This is typically used for treatment of large molecules in special process applications. They are mainly applied in enzyme purification as enzyme carriers for treatment of bio-pharmaceutical substances, and treatment of feed solutions of high color value.
| Grade Name | PA308 | PA312 | PA316 | HPA25L |
| Type | Type I | |||
| Chemical Structure | 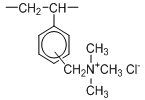 | |||
| Ionic Form As Shipped | Cl-form | |||
| Whole Bead Count | 95 min. | |||
| Shipping Density (g/L: approx.) | 710 | 675 | 670 | 675 |
| Salt Spliting Capacity (meq/mL-R) | 1.0 min | 1.2 min | 1.3 min | 0.5 min |
| Water Content (%) | 57 - 67 | 49 - 55 | 44 - 50 | 58 - 68 |
| Particle Size Distribution on 1180 μm (%) through 300 μm (%) | 5 max. 1 max. | on 300μm 5 % min | ||
| Effective Size (mm) | 0.40 min. | 0.25 min | ||
| Uniformity Coefficient | 1.6 max. | |||
| Operating Temperature (℃) | 60 (OH-form) max. 80 (Cl-form) max. | |||
| Crosslinkage (%) | Ca. 4 | Ca. 6 | Ca. 8 | - |
Porous Type BS PA400 Series (Type II)
Type II has better efficiency to be regenerated though it has lower basicity and chemical stability than Type I. PA418 is generally used in water treatment.
PA408 is used to demineralize and to decolorize sugar liquors.
| Grade Name | PA408 | PA412 | PA418 |
| Type | Type Ⅱ | ||
| Chemical Structure | 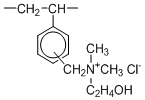 | ||
| Ionic Form As Shipped | Cl-form | ||
| Whole Bead Count | 95 min. | ||
| Shipping Density (g/L: approx.) | 720 | 685 | 685 |
| Salt Spliting Capacity (meq/mL-R) | 0.9 min | 1.1 min | 1.3 min |
| Water Content (%) | 54 - 64 | 46 - 52 | 38 - 44 |
| Particle Size Distribution on 1180 μm (%) through 300 μm (%) | 5 max. 1 max. | ||
| Effective Size (mm) | 0.40 min. | ||
| Uniformity Coefficient | 1.6 max. | ||
| Operating Temperature (℃) | 40 (OH-form) max. 60 (Cl-form) max. | ||
| Crosslinkage (%) | Ca. 4 | Ca. 6 | Ca. 9 |
Gel Type BS UBA Series
Ion exchange resins with good uniformity in particle size increase their necessity to reduce the reagents costs and spent waste waters in manufacturing pure waters. They are also used in otherfields because they have little amount of large particles easy to be broken by swelling and shrinkage. Gel type ion exchange resins of uniform particle size are now launched to meet such necessity.
| Grade Name | UBA100 | UBA120 | UBA200 |
| Type | Type Ⅰ | Type Ⅱ | |
| Chemical Structure | 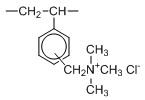 | 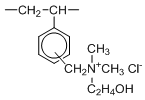 | |
| Ionic Form As Shipped | Cl-form | ||
| Whole Bead Count | 90 min. | 95 min. | 90 min. |
| Shipping Density (g/L: approx.) | 680 | 675 | 715 |
| Salt Spliting Capacity (meq/mL-R) | 1.35 min | 1.3 min | |
| Water Content (%) | 43 - 49 | 49 - 55 | 45 - 51 |
| Average Diameter (μm) | 550 ± 50 | 575 ± 50 | 575 ± 50 |
| Uniformity Coefficient | 1.1 max. | ||
| Operating Temperature (℃) | 60 max. (OH-form) 80 max. (Cl-form) | 40 max. (OH-form) 60 max. (Cl-form) | |




