The Common Types and Sizes of V-Belts

Common Types of V-Belts: Sizes, Applications & Selection Guide
Published Sep 27, 2025 • Reading time: 6 min
What Is a V-Belt?
A V-belt is a common power-transmission belt used across industrial, agricultural, and automotive equipment. The belt’s trapezoidal "V" cross-section fits into pulley grooves and creates a secure wedge action to reduce slippage.
Why Choosing The Right V-Belt Matters
Selecting the proper V-belt improves machine efficiency, reduces wear, and extends service life. Incorrect selection can cause premature failure, increased energy use, and unplanned downtime.
Main Types of V-Belts
1. Classical V-Belts
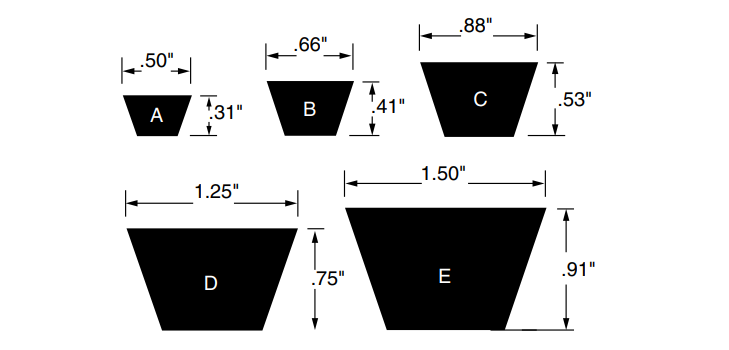
The conventional V-belt is the most common type and has been around the longest. The Initial classical V design replaced leather belts by taking over their applications in various industries, such as agriculture, ventilation, and industrial machinery. Classical V-belts can cover a load range from fractional(less than 1 HP) to 500 horsepower. They are less efficient than narrow V-belts and generally contribute to higher bearing loads. However, classical V-belts have a high tolerance for poor operating conditions. The general part number format is the cross-section size and the inside length in inches ( e.g., B50 is a B section of 50 inches inside measurement). General cross-sectional dimensions that are used in the US are shown below.

- Identification: A, B, C, D, E sections + internal length in inches (e.g., B50).
- Features: Traditional design, flexible, suitable for a wide power range.
- Applications: Fans, conveyors, agriculture equipment, HVAC drives.
2. Narrow V-Belts (Wedge Belts)
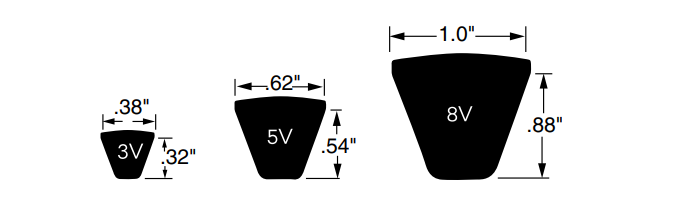
- Identification: 3V, 5V, 8V with outside length (e.g., 5V500).
- Features: Deeper profile, higher power density, works well where space is limited.
- Applications: Compressors, pumps, heavy-duty and high-speed machinery.
Note: An "X" suffix (e.g., 5VX) typically indicates a cogged (notched) belt for better flexibility and cooling.
3. Fractional Horsepower (FHP) V-Belts
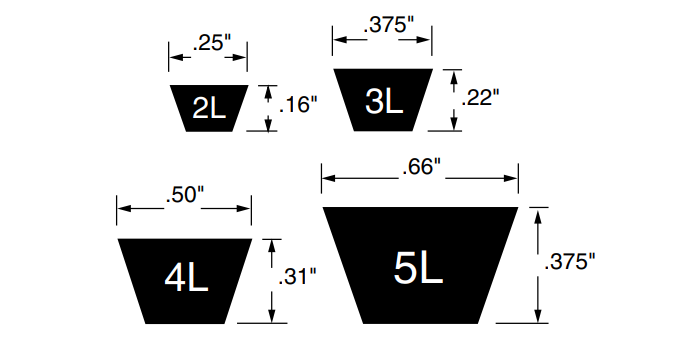
- Identification: 2L, 3L, 4L, 5L (e.g., 3L300).
- Features: Lightweight, economical, designed for low-power use.
- Applications: Household appliances, small fans, light equipment.
Quick Comparison
| Type | Example | Power | Applications | Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classical V-Belt | B50 | Low–Medium | Fans, conveyors, agriculture | Versatile & common |
| Narrow V-Belt | 5V500 | Medium–High | Compressors, pumps, heavy-duty | Higher efficiency |
| FHP V-Belt | 3L300 | Low | Small appliances, fans | Lightweight & affordable |
How to Choose the Right V-Belt
- Power & Speed: Match horsepower and RPM.
- Pulley & Shaft: Consider pulley size and belt length.
- Environment: Heat, dust, oil, moisture matter.
- Load Type: Continuous vs shock loads.
- Efficiency vs Cost: Narrow belts are efficient but more expensive.
Conclusion
V-belts remain a cost-effective and reliable choice for many power transmission applications. Knowing the differences—classical, narrow, and FHP—helps you choose the right solution for performance and efficiency.
📌 Next Steps
- Contact us for expert help
- Download V-Belt Size Chart
BOSHUO
❤️CustomizeMODAccept Customer Customized

Customize special belts for you, one-to-one comparison, improve reputation, and provide attentive service